Topic: Horner's Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 54-year-old white male presents with drooping of his right eyelid for 3 weeks. On examination, he has ptosis of the right upper lid, miosis of the right pupil, and decreased sweating on the right side of his face. Extraocular muscle movements are intact. In addition to a complete history and physical examination, which one of the following would be most appropriate at this point?
A chest radiograph
MRI of the brain and orbits
131 Iodine thyroid scanning
A fasting blood glucose level
Correct Answer :
A. A chest radiograph
The clinical triad of Horners syndromeipsilateral ptosis, miosis, and decreased facial sweating suggests decreased sympathetic innervation due to involvement of the stellate ganglion, a complication of Pancoasts superior sulcus tumors of the lung. Radiographs or MRI of the pulmonary apices and paracervical area is indicated. Horners syndrome may accompany intracranial pathology, such as the lateral medullary syndrome (Wallenbergs syndrome), but is associated with multiple other neurologic symptoms, so MRI of the brain is not indicated at this point. The acetylcholine receptor antibody level is a test for myasthenia gravis, which can also present with ptosis, but not with full-blown Horners syndrome. Diabetes mellitus and thyroid disease do not commonly present with Horners syndrome.
Related Questions
Topic: Absence Seizures
Subject: Medicine
The treatment of choice for absence seizures is:
Lamotrigine
Ethosuximide
Phenobarbital
Phenytoin
Topic: Seizure
Subject: Medicine
Of the following, which is the most frequent cause of seizures in the elderly?
Alcohol withdrawal
Stroke
Head trauma
Hypoglycemia
Topic: Analgesics
Subject: Medicine
A 74-year-old black female has moderately severe pain due to osteoarthritis. However, she is also on medication for a seizure disorder. When choosing medications to manage her chronic pain, which one of the following should be used with caution because of her history of seizures?
Salsalate (Disalcid)
Celecoxib (Celebrex)
Hydrocodone (Lortab)
Tramadol (Ultram)
Topic: Diagnostic Investigations
Subject: Medicine
A 52 year old male with a history of psychosis presents with muscle stiffness and resting tremors, associated with difficulty in balance and initiating movements. What is the best diagnostic method for detection of the above condition?
Serum dopamine levels
Computed tomography scan
Positron emission tomography scan
Magnetic resonance imaging
Topic: Seizure
Subject: Medicine
A 52-year-old man with a history of seizure attacks suffered from loss of consciousness and tonic and clonic muscular contractions. His tongue fell back into his throat and he choked. What is the best diagnostic test for assessment of the presenting condition of this patient?
X-rays
CT-Scan
Electroencephalogram
Discography
Topic: Brain Death
Subject: Medicine
A 30 year old man has been on life support systems for the past 48 hours following blunt head trauma. Brain death cannot be established in this patient if there is the presence of which of the following?
Carotid blood flow
Cremasteric reflexes
Elevated serum aminoglycoside concentrations
Hypothermia
Topic: Mini Mental Status Exam (or MMSE)
Subject: Medicine
While performing the Mini-Mental State Exam the PCP asks her patient to copy the following design. What cognitive function is being assessed by this request?
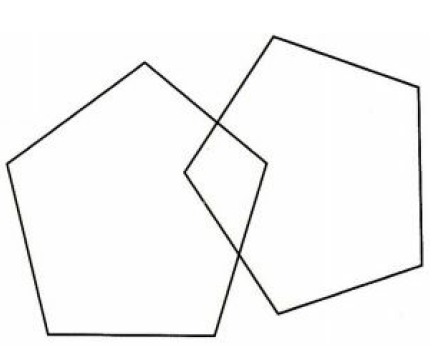
Language
Orientation
Registration
Visual-motor integrity
Topic: Brown-Sequard Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
Which of the following would not be expected in a right-sided Brown-S�quard syndrome?
Right-sided hemi-paresis
Right-sided loss of proprioception
Left-sided decreased sensitivity to pinprick
Left-sided decreased vibration sense
Topic: Guillain-Barr� syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 43-year-old man presents 2 weeks after you see him for infectious diarrhea caused by C. jejuni. He has now developed bilateral proximal lower limb weakness and bilateral distal parasthesia and decreased ankle tendon reflex.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Guillain-Barr� syndrome
Multiple Sclerosis
Myasthenia Gravis
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Topic: Cauda Equina Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 65-year-old male presents with a 1-month history of problems passing urine. He says that his bladder will feel full when he needs to urinate, but the urine stream is weak and his bladder does not feel as if it has emptied completely. The symptoms have become increasingly severe over the past week. Other symptoms include upper respiratory congestion for 3 days which he has treated with an over-thecounter decongestant with some relief, constipation with no passage of stool in the past 9 days, and increasing low back pain incompletely relieved with ibuprofen, with associated weakness in both legs. Examination shows a healthy-appearing male who is moderately overweight. He is afebrile and vital signs are normal. There is no abdominal tenderness and no masses are detected. A rectal examination reveals a large amount of hard stool in the rectum; a markedly enlarged (4+), boggy, tender prostate gland; laxity of the anal sphincter; and numbness in the perianal area. Urinalysis shows trace protein and 10-20 WBCs/hpf. Ultrasonography shows a post-void residual volume of 250 mL (normal for age <100).
Which one of the following must be done urgently in this patient?
Foley catheterization
Hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics
Digital disimpaction of the rectum, and Fleet enemas until clear
MRI of the lumbosacral spine
Topic: Bell's Palsy
Subject: Medicine
A 53-year-old male accountant comes to your office with progressive facial weakness on the left side that began yesterday. He also reports pain behind the left ear and decreased lacrimation from the left eye. He has been in good health and had his yearly physical examination 1 week ago, which was normal. His lipid levels, chemistry profile, and CBC were all normal. He has not been involved in any outdoor activities, nor does he engage in any high-risk sexual behavior. On examination, there is flattening of the left nasolabial fold and decreased ability to close the left eye. The mouth appears to be drawn to the right. The remainder of his general examination and neurologic examination are normal.
Which one of the following would be the most appropriate management at this time?
Carotid ultrasonography
High-resolution CT
MRI with gadolinium enhancement
Prednisone and valacyclovir (Valtrex)
Topic: Peripheral Neuropathy
Subject: Medicine
A 68-year-old male presents to your department complaining of a very horrible sensation in his legs that started out 4 weeks ago as pins and needles tickling him but now has progressed and feels like being stabbed in his feet. He has started to use a walker because he feels that when he walks it feels like stepping on eggshells. The pain has not been responsive to acetaminophen and ibuprofen. The patients past medical history is significant for diabetes type II treated with metformin and glimepiride. The patient has not been very compliant with medications, especially metformin because he feels it causes him an upset stomach. His most recent HbA1C level was 9.8%. He also has hypercholesterolemia treated with lovastatin and hypertension treated with Lisinopril and amlodipine. His vital signs are temperature 37.4°C, BP is 125/70 mmHg, pulse 85/min, and respirations 15/min. The dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses are +2 bilaterally. No distal muscles weakness or atrophy is observed. Manual esthesiometer with monofilaments is used and reveals decreased sensation from the midfoot distally on both feet. There is no evidence of erythema, edema, or any wounds on either foot. He has tenderness to light touch on both feet. Labs reveal normal Vitamin B12 and thyroid function.
Which of the following would be the most appropriate treatment for this patients pain?
Daily metformin compliance
Metoclopramide
Pregabalin
Alpha lipoic acid
Topic: Benign Positional Vertigo
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following is characteristic of benign positional vertigo?
A duration of 10-15 minutes
Associated hearing loss and tinnitus
Associated diplopia and facial numbness
Being triggered by turning the head
Topic: Glasgow Coma Scale
Subject: Medicine
A 27 year old man is brought into the ER after a bicycling accident. A car door suddenly opened in front of him, of which he smashed into and was thrown 15 feet. On examination, he is drowsy and confused. He opens his eyes when his name is called. When he speaks, you understand his words but the sentences do not make sense. He moves all four limbs but does not respond to any commands. He is able to pull both hands away when pinched and squirms when his sternum is rubbed, making no effort to stop you.
What is his Glasgow Coma Scale score?
11
10
9
8
Topic: Horner's Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 66-year-old diabetic man presents with constriction of the pupil, drooping of the upper lid, and anhidrosis on the left. Which one of the following nerves is most likely involved?
Oculomotor
Sympathetic
Trochlear
Trigeminal
Topic: Status Epilepticus
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following should be given intravenously in the initial treatment of status epilepticus?
Propofol (Diprivan)
Phenobarbital
Lorazepam (Ativan)
Midazolam (Versed)
Topic: Horner's Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 54-year-old white male presents with drooping of his right eyelid for 3 weeks. On examination, he has ptosis of the right upper lid, miosis of the right pupil, and decreased sweating on the right side of his face. Extraocular muscle movements are intact. In addition to a complete history and physical examination, which one of the following would be most appropriate at this point?
A chest radiograph
MRI of the brain and orbits
131 Iodine thyroid scanning
A fasting blood glucose level
Topic: Status Epilepticus
Subject: Medicine
A 58-year-old male with a history of seizure attacks suffered from a 30 min loss of consciousness with repetitive seizures with no recovery of consciousness between attacks. What is the disorder this patient is suffering from?
Tonic-clonic seizure
Absence seizure
Atonic seizure
Status epilepticus
Topic: Essential Tremor
Subject: Medicine
A 75 year old white male complains of a tremor which has been progressive over the past 2 years. The tremor interferes with writing, pouring liquids, and eating soup. He has no other medical problems. He abstains from alcohol and tobacco products. Physical examination is remarkable for an action tremor of the upper extremities and a head tremor. No rigidity or gait disorder is noted. Of the following agents, which one is most appropriate as initial drug therapy for this problem?
Alprazolam (Xanax)
Clonazepam (Klonopin)
Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
Propranolol (Inderal)
Topic: Horner's Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 70-year-old man presented with ptosis, myosis and anhydrosis on the left side. Which one of the following is the most likely cause of this condition?
Tumour induced exophthalmos
Fourth cranial nerve palsy
Apical pulmonary carcinoma
Enlarged thyroid gland
Topic: Seizure
Subject: Medicine
A 75-year-old male is brought to your office 1 month after a stroke that involved the left anterior cerebral artery, manifested by leg weakness, initial incontinence, and slowness in mentation. He experienced seizure activity on the second day after his stroke, but this was controlled by phenytoin (Dilantin). He has improved significantly and is now ambulatory. His family states that he now has episodic confusion, sleepiness, and clumsiness, which is preceded by paresthesias and dizziness, although no tonicclonic activity has been noted. He remains very drowsy for several hours after these episodes. He was wearing a cardiac monitor during one episode, but it showed nothing remarkable. His phenytoin level is therapeutic, and a CBC, metabolic profile, and magnesium level are all normal.
Which one of the following would be the most appropriate next step?
Discontinue the phenytoin
Add phenobarbital to the phenytoin
Begin bupropion (Wellbutrin)
Begin lamotrigine (Lamictal)
Topic: Dementia
Subject: Medicine
A 60-year-old white female presents for her annual physical examination. She tells you that since her last visit she has begun taking ginkgo biloba to improve her memory. She takes no other medications. The evidence supporting a benefit from ginkgo biloba is best for which one of the following?
Tinnitus
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Dementia
Intermittent claudication
Topic: Status Epilepticus
Subject: Medicine
A 58-year-old male with a history of seizure attacks suffered from a 30min loss of consciousness with repetitive seizures with no recovery of consciousness between attacks. What is the best initial treatment for his condition?
Lorazepam
Phenytoin
Phenobarbital
Carbamazepine
Topic: Dementia
Subject: Medicine
Clinical features of multi-infarct dementia may include all of the following, except:
Parkinsonism
Deteriorating course
Evidence of cerebrovascular disease
Focal neurologic signs
Topic: Brain Death
Subject: Medicine
A 57-year-old white male with coronary artery disease suffered a cardiac arrest while jogging 10 days ago. He was resuscitated after 45 minutes but has remained unresponsive and on a ventilator since then.
Which one of the following is required to diagnose brain death in this patient?
Hypothermia
Continuous mechanical ventilation
The absence of spontaneous body movements
Electroencephalographic confirmation
Topic: Dementia
Subject: Medicine
An 85 year old white male is brought to you for the first time by his son. The father has recently seen a neurologist who performed a workup for dementia and diagnosed moderate Alzheimers disease. Which one of the following is true regarding the use of a cholinesterase inhibitor in this patient?
It is too late to initiate cholinesterase therapy
Agitation is often intensified by these agents
Memory is likely to improve significantly
Nursing-home placement may be delayed a year or longer
Topic: Alzheimer's Disease
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following is most predictive of the progression from mild cognitive impairment to frank Alzheimers dementia?
Self-reported memory deficits
Memory deficits reported by a family member
A normal MRI scan of the brain
The absence of the apolipoprotein E4 allele
Topic: Adverse Drug Effect
Subject: Medicine
A 68-year-old man with a history of urolithiasis, suffered from a seizure attack which involved loss of consciousness with tonic and clonic muscular contractions. His tongue fell back into his throat and he choked. He is treated with valproic acid.
What are the most common side effects caused by this medication?
Weight gain
Rash
Nausea and headache
Tardive dyskinesia
Topic: Trigeminal Neuralgia
Subject: Medicine
A man complains that recently when he shaves he has a shooting type of pain in his face. It happens once in a while and then goes away. You suspect trigeminal neuralgia.
What is the treatment of choice?
Fluoxetine
Prednisone
Acyclovir
Carbamazepine
Topic: Huntington Chorea
Subject: Medicine
A patient previously diagnosed with Huntington chorea (HC) comes for a family planning consult with his wife. He states that his father had the disease and his mother was unaffected. They ask you what is the likelihood having a son with this condition?
Zero
25%
50%
75%
