According to Kelvin-Planck's statement, a perpetual motion of the __________ is impossible.
First kind
Second kind
Third kind
None of these
Correct Answer :
B. Second kind
Related Questions
The shear force at the centre of a simply supported beam with a gradually varying load from zero at both ends to w per metre at the centre, is
Zero
wl/4
wl/2
wl²/2
The gas constant (R) is equal to the
Sum of two specific heats
Difference of two specific heats
Product of two specific heats
Ratio of two specific heats
A shaft revolving at ω rad/s transmits torque (T) in Nm. The power developed is
T.ω watts
2π. T.ω watts
2π. T.ω/75 watts
2π. T.ω/4500 watts
The air standard efficiency of an Otto cycle is given by (where r = Compression ratio, and γ = Ratio of specific heats)
1 - rγ - 1
1 + rγ - 1
1 - (1/ rγ - 1)
1 + (1/ rγ - 1)
Which of the following gas has the highest calorific value?
Coal gas
Producer gas
Mond gas
Blast furnace gas
Brayton cycle consists' of following four processes
Two isothermals and two isentropic
Two isentropic and two constant volumes
Two isentropic, one constant volume and one constant pressure
Two isentropic and two constant pressures
The thermodynamic difference between a Rankine cycle working with saturated steam and the Carnot cycle is that
Carnot cycle can't work with saturated steam
Heat is supplied to water at temperature below the maximum temperature of the cycle
A Rankine cycle receives heat at two places
Rankine cycle is hypothetical
When a closely-coiled helical spring of mean diameter (D) is subjected to an axial load (W), the stiffness of the spring is given by
Cd⁴/D3n
Cd⁴/2D3n
Cd⁴/4D3n
Cd⁴/8D3n
Which of the following has the minimum atomic mass?
Oxygen
Sulphur
Nitrogen
Carbon
The ratio of the largest load in a test to the original cross-sectional area of the test piece is called
Elastic limit
Yield stress
Ultimate stress
Breaking stress
One kg of ethylene (C2H4) requires 2 kg of oxygen and produces 22/7 kg of carbon dioxide and __________ kg of water or steam.
9/7
11/7
7/4
1/4
The ratio of maximum shear stress developed in a rectangular beam and a circular beam of the same cross-sectional area is
2/3
3/4
1
9/8
The molecular mass expressed in gram (i.e. 1 g - mole) of all gases, at N. T. P., occupies a volume of
0.224 litres
2.24 litres
22.4 litres
224 litres
Euler's formula holds good only for
Short columns
Long columns
Both short and long columns
Weak columns
A simply supported beam with a gradually varying load from zero at B and w per unit length at A is shown in the below figure. The shear force at B is equal to
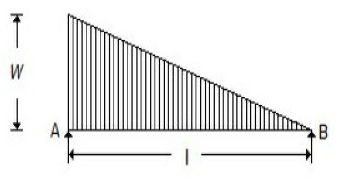
wl/6
wl/3
wl
2wl/3
In a reversible adiabatic process, the ratio of T1/T2 is equal to
(p2/p1)γ - 1/ γ
(p1/p2)γ - 1/ γ
(v2/v1)γ - 1/ γ
(v1/v2)γ - 1/ γ
The ratio of specific heat at constant pressure (cp) and specific heat at constant volume (cv) is always __________ one.
Equal to
Less than
Greater than
None of these
The efficiency of Diesel cycle with decrease in cut-off
Increases
Decreases
First increases and then decreases
First decreases and then increases
One kg of hydrogen requires 8 kg of oxygen and produces
1 kg of water
7 kg of water
8 kg of water
9 kg of water
The materials which exhibit the same elastic properties in all directions are called
Homogeneous
Inelastic
Isotropic
Isentropic
For which material the Poisson's ratio is more than unity
Steel
Copper
Aluminium
None of the above
Which of the following is an intensive property of a thermodynamic system?
Volume
Temperature
Mass
Energy
One kg of carbon monoxide requires 4/7 kg of oxygen and produces
11/3 kg of carbon dioxide gas
7/3 kg of carbon monoxide gas
11/7 kg of carbon dioxide gas
8/3 kg of carbon monoxide gas
The heat and mechanical energies are mutually convertible. This statement was established by
Boyle
Charles
Joule
None of these
Tensile strength of a material is obtained by dividing the maximum load during the test by the
Area at the time of fracture
Original cross-sectional area
Average of (A) and (B)
Minimum area after fracture
A tri-atomic molecule consists of __________ atoms.
One
Two
Three
Four
When a gas is heated at constant volume
Its temperature will increase
Its pressure will increase
Both temperature and pressure will increase
Neither temperature nor pressure will increase
In an ideal gas turbine plant, it is assumed that the compression and expansion processes are
Isothermal
Isentropic
Polytropic
None of these
The __________ states that change of internal energy of a perfect gas is directly proportional to the change of temperature.
Boyle's law
Charle's law
Gay-Lussac law
Joule's law
The relation between equivalent length (L) and actual length (l) of a column for both ends fixed is
L = l/2
L = l/√2
L = l
L = 2l
